Author: Tom Frampton
Source
View Tom Frampton on Plugin Boutique
Elevate your mixing workflow with the SSL autoSeries Bundle, a powerhouse collection of Solid State Logic’s most intuitive processors. Featuring the acclaimed Vocalstrip 2 and Drumstrip, this bundle provides the essential tools to achieve professional-grade clarity and punch with legendary SSL sonic character.
Introduction
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in various sectors has been nothing short of a revolutionary whirlwind, altering landscapes of industries from healthcare to finance. But nowhere does this integration feel more like a dramatic symphony than in the world of music production. AI’s foray into this creative domain isn’t just a story of technological evolution; it’s a fascinating tale of how the very essence of music creation is being re-examined and redefined.

AI’s Evolution in the Music Industry: From Backstage to Center Stage
AI, initially perceived as a cluster of complex algorithms suitable for computational tasks, has gradually morphed into a versatile artist in the music industry. From the days when music production was synonymous with tangible instruments and recording studios lined with analog equipment, we’ve entered an era where digital technologies, and specifically AI, have become integral to how music is created, produced, and even consumed.

Interest in AI Music peaked in April 2023 but remains high.
A New Frontier or an Age-Old Debate in a New Guise?
The integration of AI in music production sparks a debate as old as innovation itself: Do new technologies enhance the artist’s toolkit, or do they threaten the very soul of artistic authenticity? In this blog post, we’ll explore this intricate dance between AI and music producers. Is AI stepping on the toes of traditional composers, or is it waltzing seamlessly with them, leading to a new era of collaborative creation?
What to Expect
As we delve into this rhythm of revolution, expect to uncover:
- The Journey of AI in Music: How has AI evolved from a mere experimental tool to a potential maestro in the studio?
- AI as a Threat or an Ally: We’ll dissect whether AI is indeed snatching the baton from human hands or if it’s empowering composers to reach new creative heights.
- Ethical and Artistic Implications: Navigate through the murky waters of copyright, originality, and the artistic implications of AI in music.
- Preparing for a Harmonious Future: How can today’s music producers leverage AI for innovation while keeping the human spirit of music alive?

So, whether you’re a music producer, an AI enthusiast, or just a curious bystander in this symphonic interplay of technology and creativity, this post promises insights, debates, and maybe a new perspective on the role of AI in music production.
Tune your senses to this exploration, and let’s find out if AI in music production is a threat looming on the horizon or a companion walking beside us into a new era of musical innovation.
Section 1: The Advent of AI in Music
The journey from vinyl to virtual reality in music production has been a blend of breakthroughs and bold ventures, but the entrance of AI into this arena could very well be the crescendo we didn’t see coming.
A Symphony of Progress: The History of Technology in Music
Let’s rewind the tape a bit. The history of music production is a testament to constant innovation. From the invention of the phonograph in the late 19th century to the synthesizers of the 1960s, each technological advancement redefined what music could be. The digital age accelerated this evolution exponentially, with computers, software synthesizers, and digital audio workstations (DAWs) transforming mere sounds into rich, complex musical compositions. The digital revolution set the stage for something even bigger, paving the way for AI’s debut in music production.
AI Enters the Studio: A New Composition Begins
The introduction of AI in music isn’t just a new chapter; it’s almost like a new genre. Initially, AI’s role was confined to algorithms that could recommend music based on listener preferences or master tracks with subtle precision. However, the turn of the millennium saw AI stepping directly into the shoes of a composer and producer.
Machine learning models, trained on vast datasets of existing music, began to understand and replicate complex musical structures, creating compositions that blurred the lines between human and computer-generated music. Tools like Google’s Magenta, based on TensorFlow, started not just mimicking existing music but generating novel compositions, opening a Pandora’s box of creative and philosophical questions about the nature of art and creation.
AI Tools Hitting the High Notes
In today’s studios, AI’s presence is both nuanced and notable. From AI-driven plugins that enhance mixing and mastering to sophisticated algorithms writing entire pieces, the spectrum of AI’s involvement is vast. Tools like IBM’s Watson Beat, AIVA (Artificial Intelligence Virtual Artist), and Amper Music are not only aiding composers in fleshing out ideas but also generating complete tracks that challenge our traditional notions of composition and creativity.

Stats on AI Adoption Among Music Producers
- 60% of musicians are already using AI to make music in some capacity, whether for mastering, generating artwork, or composing.
- 20.3% of artists have used AI for music production.
- 30.6% of artists have used AI for mastering.
- 38% of artists have used AI for artwork.
- 40% view AI positively, and 39% believe it suits their goals. So while some fear replacement, most see AI as a collaborative tool.
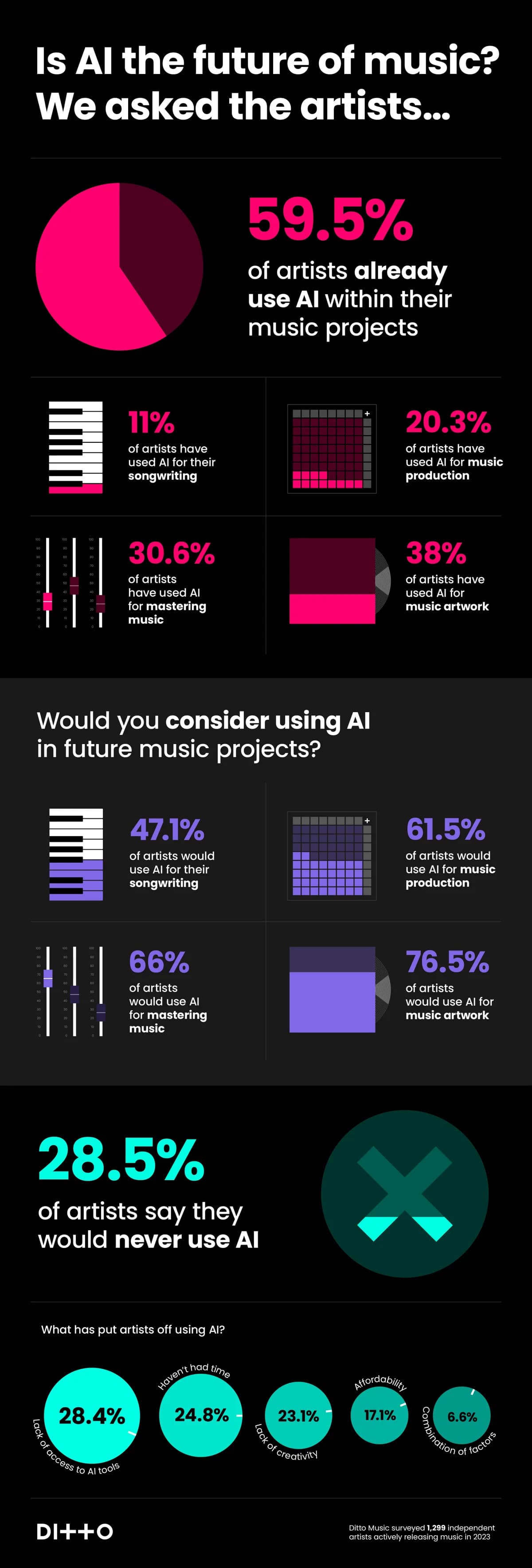
The statistics paint a clear picture: AI in music production isn’t just a fleeting trend; it’s reshaping the landscape in ways we’re just beginning to comprehend. As AI continues to harmonize with traditional music production methods, it’s essential to ask: Is AI’s role in music merely about enhancing human creativity, or is it overshadowing the human element altogether?
In the next section, we’ll tune into this debate, examining AI not only as a tool but as a potential titan in the arena of musical composition.
Section 2: AI as the Composer’s Competitor
The notion of AI as a potential rival to human composers isn’t just a speculative thought; it’s a discussion echoing through the halls of recording studios and music academies alike. But how real is this threat?
The Fear Factor: AI Replacing Human Composers
The fear that AI might render human composers obsolete isn’t unfounded. With AI systems like OpenAI’s Jukebox composing songs that mimic styles ranging from Elvis Presley to Katy Perry, the lines are blurring. Albums like “I AM AI,” produced by YouTube star Taryn Southern with the aid of Amper Music’s AI, further fuel the debate. These aren’t just algorithmic experiments but commercially viable tracks challenging the notion of authorship and creativity in music.
The Capabilities and Limitations of AI in Composing
To understand the potential threat of AI, we must dissect what AI can realistically achieve. AI excels at pattern recognition, learning from existing musical structures, and creating compositions based on these datasets. However, AI’s ability to evoke deep emotional resonance, a hallmark of great music, remains debatable.
Can AI Capture Human Emotion?
Music, at its core, is an expression of human emotion and experience. While AI can replicate styles and structures, the jury is still out on whether it can truly capture the spontaneous burst of human feelings and the storytelling aspect that human composers bring to their music.
The debate brings us to a crucial juncture: Is the fear of AI replacing human composers justified, or are we witnessing a new kind of partnership in the making? Perhaps, the real question is not about replacement but about transformation and evolution.
In the upcoming section, we’ll shift the lens to view AI not just as a rival but as a potential collaborator in the creative process. We’ll explore how this technology, often seen as a competitor, could in fact be a powerful ally for musical innovation.

Section 3: AI as the Creative Partner
Rather than viewing AI solely as a threat to traditional composition, it’s worth exploring its role as a dynamic ally in the creative process. How is this technological marvel reshaping music production, not by replacing, but by augmenting human creativity?
Redefining the Creative Process
The advent of AI in music production is less about the robot apocalypse and more about a renaissance in creativity. AI tools provide a new palette for composers to experiment with sounds and structures that might be beyond human reach.
Real-World Examples
- AI in Songwriting and Arrangement: Artists like Holly Herndon have integrated AI into their creative process, using it to generate unique vocal and harmonic elements.
- Enhancing Production: AI algorithms help fine-tune equalization, dynamics, and sonic textures, allowing producers to focus on the creative aspects of production.
Insights from the Trenches: How Professionals are Using AI
The real magic happens when human expertise meets AI efficiency. Music producers increasingly view AI as a collaborator, an entity that brings a new dimension to their creative arsenal.

Top 5 AI Tools for Music Production
- Amper Music: An AI tool that composes and produces unique music pieces based on user inputs.
- AIVA: An AI software specializing in creating emotional and cinematic soundtracks.
- Google’s Magenta: An open-source project exploring the role of AI in art and music creation.
- IBM Watson Beat: An AI capable of making music with a more human feel.
- LANDR: Uses AI for mastering tracks, offering quick and tailored mastering.
AI, in these scenarios, isn’t a soloist taking center stage but more of a section player in an orchestra, adding depth and dimension while being guided by the human conductor.
Transitioning from Competition to Collaboration
The evolution from seeing AI as a competitor to a collaborative partner involves a paradigm shift. It’s about recognizing AI’s role as a tool in the artist’s kit – one that can open doors to uncharted musical territories.
The Producer’s Perspective
Embracing AI in music production can be empowering rather than threatening. It offers an opportunity to break free from traditional confines, pushing the boundaries of creativity and innovation. The key lies in using AI to do what it does best – managing data, identifying patterns, and executing repetitive tasks – thereby freeing the human artist to focus on the heart and soul of music: emotion and storytelling.
As we move forward, the partnership between AI and human creativity in music seems not just inevitable but potentially fruitful. In the next section, we’ll delve deeper into the ethical and artistic implications of this relationship, exploring the balance between technological advancement and artistic integrity.

Section 4: Ethical and Artistic Implications in AI-Mediated Music
The rise of AI in music production isn’t just a technological and creative shift; it also brings forth a myriad of ethical and artistic implications that warrant a closer look.
The Question of Originality and Copyright
One of the most pressing concerns in the realm of AI-generated music revolves around originality and copyright. Who owns a piece of music when it’s composed by AI based on learning from thousands of existing works?
Legal Perspectives
Copyright Challenges: The legal system is still catching up with the complexities introduced by AI in music. Determining the copyright of AI-created music, especially when it’s influenced by existing human compositions, remains a grey area.
The Authenticity of Art
Beyond the legalities, there’s an artistic debate simmering beneath the surface. Can music created with the help of AI be considered ‘authentic’? This debate taps into deeper questions about art and technology.
Philosophical Musings
Artistic Merit: Discussions around whether AI-composed music can be considered art, or if it’s merely a technological output, are ongoing.
The Human Touch: Many argue that the soul of music lies in its imperfections and human nuances, something an AI might not be able to replicate.

Ethics in AI Use
How ethical is the use of AI in music production? This question covers not only the creation of the music but also the data used to train these AI systems.
Data Transparency: Understanding where and how the training data for AI systems is sourced is crucial. There are concerns about consent and acknowledgment when it comes to using existing tracks for training purposes.
Bias and Diversity: AI systems are only as unbiased as the data they’re fed. There’s a risk of perpetuating existing biases in genre, style, or cultural representation in music if AI isn’t trained on diverse datasets.
Navigating these ethical and artistic complexities is crucial as we integrate AI more deeply into the music production process. Recognizing and addressing these concerns is not just about safeguarding human creativity but also about ensuring fairness, originality, and diversity in the music industry.
In the next section, we’ll conclude by looking towards the future – pondering over how to best prepare for an era where AI is an undeniable part of the music production landscape, ensuring a harmonious balance between technological innovation and the timeless human essence of music.
Section 5: Embracing the Future: Finding Balance in the AI-Music Equation
As we stand on the cusp of a new era in music production, the integration of AI isn’t just inevitable; it’s already happening. The challenge now is not in resisting this wave but in learning how to surf it with skill and ethical consideration.
Preparing for an AI-Enhanced Music Industry
Embracing AI in music production requires a blend of openness, awareness, and strategic thinking. For the contemporary music producer, staying informed and adaptable is key.
Adapting Skills and Knowledge
Continuous Learning: Keeping up with the latest AI advancements and tools is essential. Understanding the mechanics and capabilities of AI in music can empower producers to use these tools effectively and creatively.
Skill Diversification: Encouraging a broader skill set that goes beyond traditional music production, including AI programming and data analytics, can offer producers a significant edge.

The Future of Music Production with AI
Looking ahead, the role of AI in music is set to expand, bringing both challenges and opportunities. Predictions about AI’s future impact range from complete automation of certain production processes to new forms of interactive and adaptive music experiences.
Trends to Watch
Interactive Music Experiences: AI might lead to more immersive and interactive music experiences, adapting to listeners’ environments or emotional states.
Automation in Production: Certain aspects of music production, particularly technical tasks like mixing and mastering, are likely to see increased automation.
Ethical and Artistic Harmony
As AI becomes more entrenched in the music industry, maintaining an ethical and artistic balance is paramount. This involves conscious decision-making about how AI is used and an ongoing dialogue about its implications in the industry.
Strategies for Balance
Ethical Frameworks: Developing and adhering to ethical guidelines around AI use in music production, including issues like data privacy, copyright, and representation.
Celebrating Human Element: Ensuring that the unique qualities of human-created music are valued and preserved alongside AI-generated compositions.

In conclusion, the rise of AI in music production isn’t a zero-sum game where the entry of AI spells the exit of human creativity. Instead, it’s an evolving symphony where human ingenuity harmonizes with technological advancement, leading to new heights of creative expression.
As we navigate this new terrain, the focus should be on leveraging AI’s strengths to enhance and expand the human creative spirit, rather than replacing it.
Conclusion: Harmonizing AI with the Human Touch in Music
As we’ve journeyed through the evolving landscape of AI in music production, it’s clear that this technological advancement is neither a panacea nor a peril but a powerful tool that, when used wisely, can enrich the music industry in unprecedented ways.
The Key Takeaways
AI as a Catalyst, Not a Replacement: AI should be seen as a catalyst that can spur creativity, efficiency, and innovation in music production, rather than a replacement for the human composer.
Balancing Act: The true artistry in the age of AI will lie in balancing the technical prowess of AI with the irreplaceable depth, emotion, and intuition of human creativity.
Ethical Considerations are Crucial: Addressing the ethical implications, from copyright issues to ensuring diversity and bias mitigation in AI-generated music, is essential for a responsible evolution in the industry.
Embracing the Future
The future of music production, shaped by AI, offers exciting possibilities. From enhanced creative processes and new sounds to more efficient workflows, the potential is enormous. However, this new era also demands a more nuanced understanding and a thoughtful approach.
Moving Forward
Collaboration Over Competition: Viewing AI as a collaborator and not a competitor can lead to more innovative and groundbreaking music production.
Continued Learning and Adaptation: Staying abreast of technological developments and continuously adapting one’s skills will be key to thriving in this new landscape.
Preserving the Human Essence: Amidst technological advancements, preserving the human essence in music — the raw emotion, storytelling, and connection — remains paramount.

Final Thoughts
AI in music production is not about ushering in a cold, robotic future; it’s about opening doors to new creative realms. It’s an invitation to rethink and expand our artistic boundaries, where the combination of human and machine intelligence can lead to musical expressions yet unheard and unimagined. As we embrace this partnership, we may find that the greatest compositions lie not in human or machine alone, but in the harmony of their collaborative symphony.





